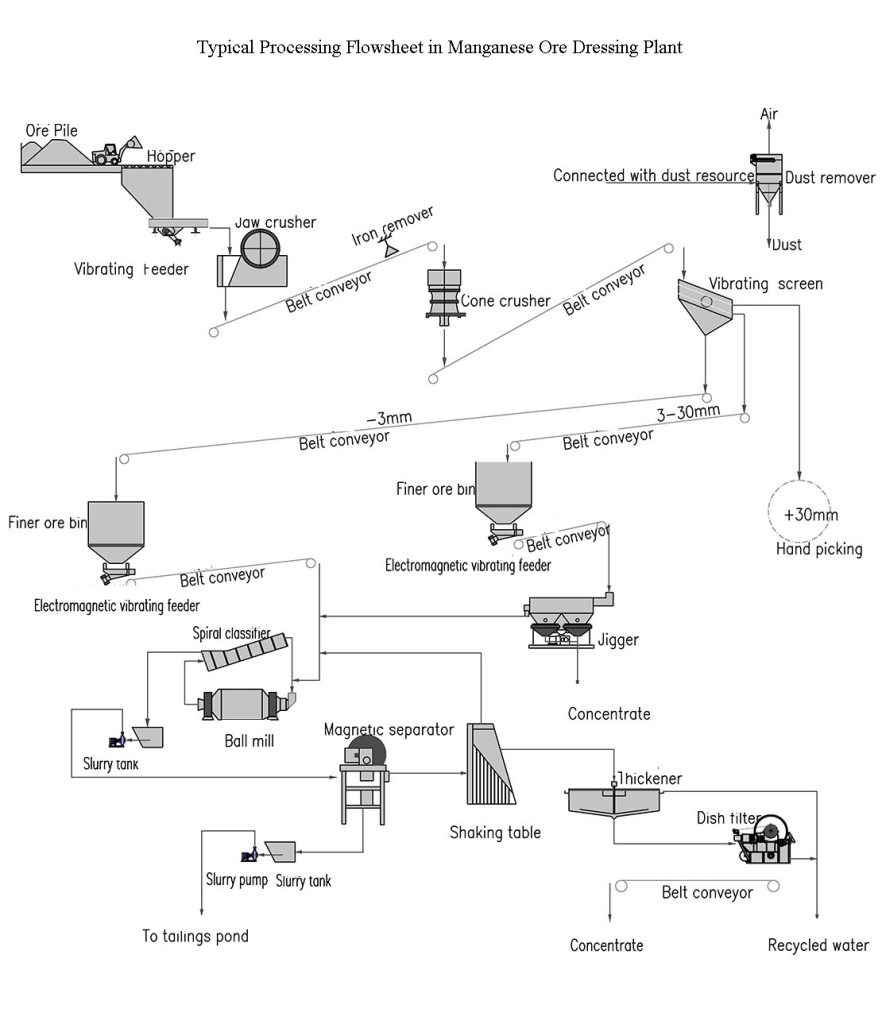
Manganese ore resources are diverse and complex. To obtain high-grade and high-recovery concentrates, the ore usually needs to undergo systematic processes such as crushing, screening, grinding, separation, and smelting. Below is the typical manganese ore beneficiation and processing flow:
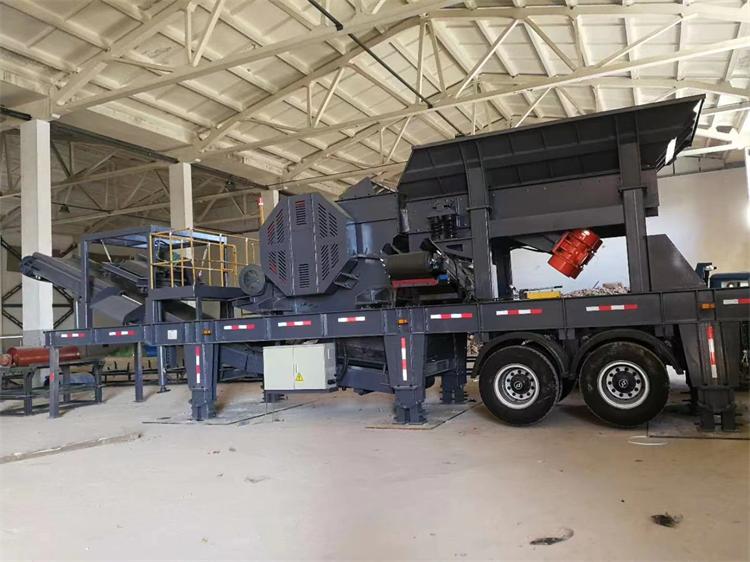
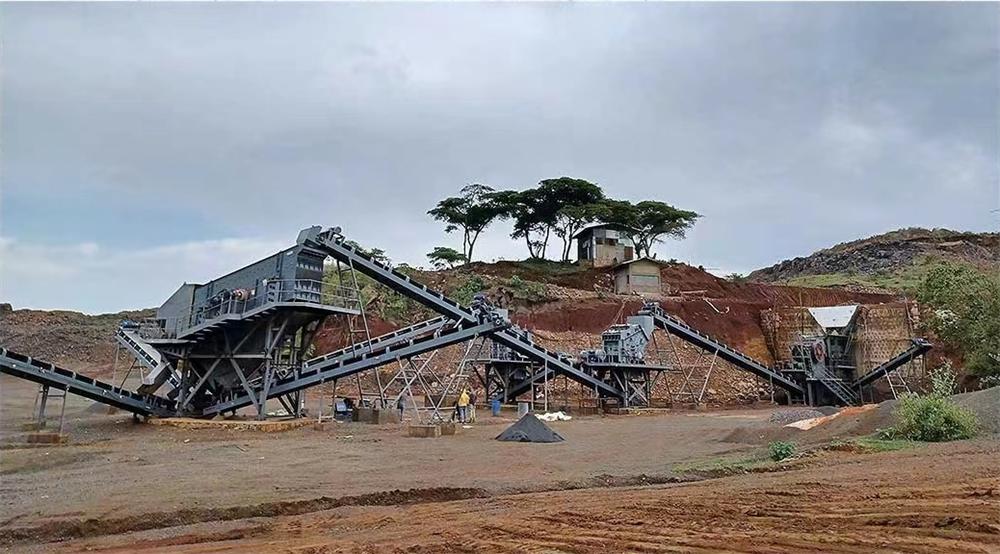
1. Crushing & Screening
Large raw manganese ore is first crushed using primary crushers such as jaw crushers, followed by secondary crushing with impact or cone crushers.
After crushing, vibrating screens classify the ore into different size fractions. Coarse particles return to the crushing system, while finer particles proceed to grinding or separation.
The goal of this stage is to ensure uniform particle size distribution for the next process.
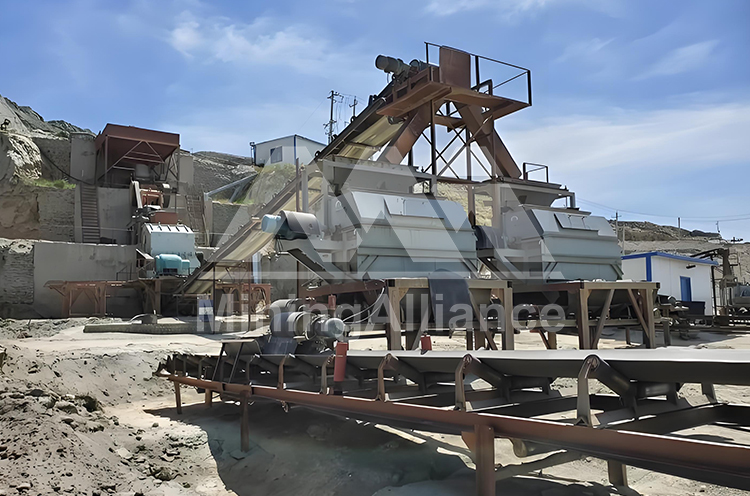

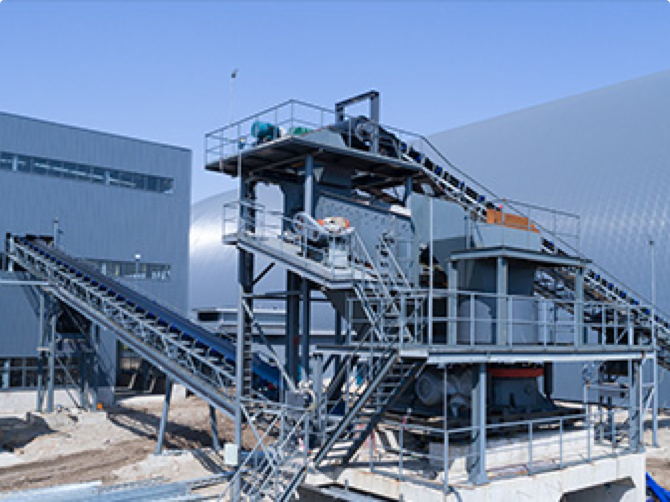
2. Grinding
For ores with fine dissemination, grinding is essential. Ball mills or rod mills are used to achieve full liberation of manganese minerals.
The ground ore slurry is usually controlled at a size below 0.2–0.3 mm, preparing it for magnetic, gravity, or flotation separation.
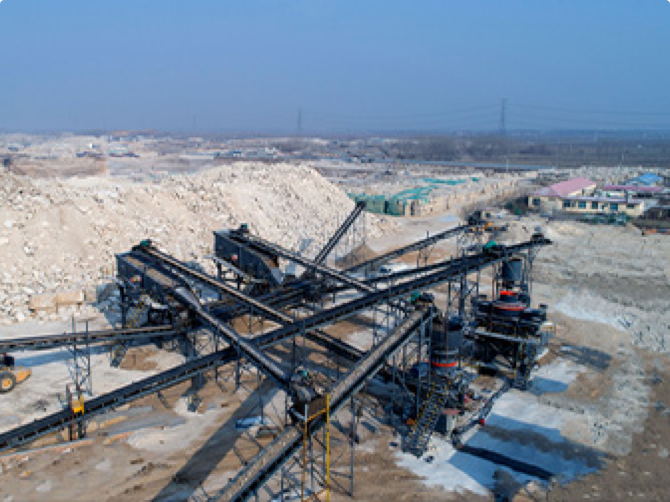
3. Separation Process
Different beneficiation methods are applied depending on the ore type:
- Strong Magnetic Separation: Effective for carbonate manganese ore and some oxide ores.
- Dense-Media & Gravity Separation: Using jigs and shaking tables, suitable for blocky and coarse-grained ores.
- Flotation: Mainly used for sulfur-carbonate manganese ore and hydrothermal ores to remove pyrite, sphalerite, or galena.
- Roasting–Magnetic Separation: Applied to manganese-sulfur ores, where roasting removes sulfur and volatile components before further separation.
4. Ore Washing & Desliming
For weathered oxide manganese ores with high mud content, ore washing is necessary.
Washing drums and spiral washers remove clay and fine slimes, often combined with overflow classification to improve concentrate grade.
5. Concentrate Treatment & Smelting
Even after beneficiation, some concentrates require smelting to remove impurities like iron, phosphorus, and sulfur.
Smelting methods include blast furnace and electric furnace processes, producing manganese products suitable for steelmaking, chemical industry, and battery materials.